What is Lactide?
Futeon™ LD: A bio-based building block
Lactide is a cyclic di-ester formed by condensing two lactic acid molecules. This process releases water and creates a cyclic molecule known as lactide. It exists in three isomeric forms due to the chiral nature of lactic acid: L-, D-, and meso-lactide.
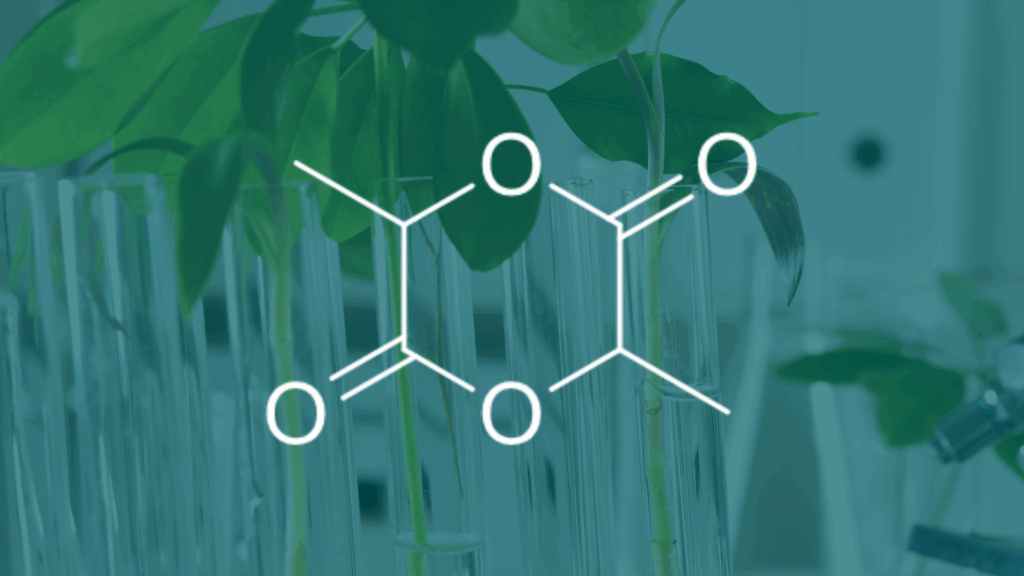
What is Lactide?
Main Applications of Lactide
Lactide is primarily used for synthesising high molar mass PLA, which has a wide range of applications.
Lactide can be used to produce new materials. Copolymerisation of lactide with another monomer can result in a polymer with tailored properties such as increased flexibility, toughness and degradation rate. Some examples of copolymers:
- PLGA: Lactide can be copolymerized with glycolide to form poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), which is another biodegradable polymer
- PLCL: Lactide can be copolymerized with caprolactone to form poly-lactide-co-caprolactone (PLCL), which is a biodegradable polymer with improved mechanical properties compared to traditional PLA
- PLTMC: Lactide can be copolymerised with trimethylene carbonate to form poly-lactide-co-trimethylene carbonate, which is a biodegradable polymer with improved flexibility compared to traditional PLA
Our portfolio
Futerro can provide further information on our grades of Futeon™ LD based on request. Please contact directly our sales department.
